The second edition of the “Lifestyle, Diet, Wine & Health” congress, partnered with Science and Wine, will be held in Rome, Italy from March 26-28, 2025. This international event brings together leading scientists to present the latest research on healthy lifestyles, combining information on active living, balanced Mediterranean-style diets, and moderate wine consumption.
Neuroprotective Effects of Olive Oil: A Comprehensive Review of Antioxidant Properties
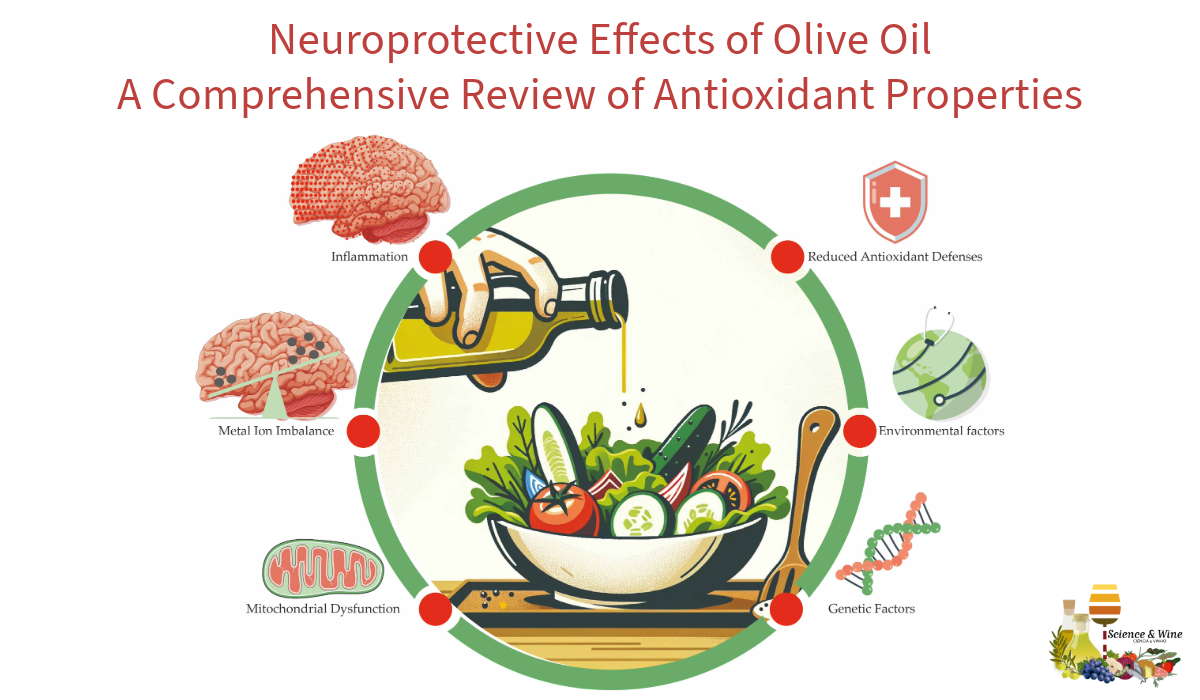
Neurodegenerative diseases driven by oxidative stress pose significant global health challenges. “Neuroprotective Effects of Olive Oil: A Comprehensive Review of Antioxidant Properties,” published in Antioxidants (MDPI), explores olive oil’s potential in combating these diseases through its antioxidants—oleuropein, hydroxytyrosol, and oleocanthal. These compounds reduce oxidative stress and inflammation while improving mitochondrial function. Incorporating olive oil into dietary patterns, particularly in the Mediterranean diet, is associated with a lower risk of neurodegenerative diseases. However, long-term clinical trials are required to translate these benefits into practical dietary recommendations. This review highlights the promising role of olive oil in preventive neurology, by reducing the risk of neurodegenerative conditions through its potent antioxidant properties.

Low-Alcohol and Nonalcoholic Wines: From Production to Cardiovascular Health, along with Their Economic Effects
The emergence of nonalcoholic wines is driven by health, economic, and social factors, meeting growing consumer interest in healthier lifestyles. The health benefits of low-alcohol and nonalcoholic wines, particularly cardiovascular health, are increasingly recognized. Winemakers can diversify their product lines using these alternatives, extend their customer base, and contribute to public health. Advanced production techniques such as vacuum distillation, spinning cone columns, and reverse osmosis reduce alcohol content without compromising quality. The expanding market for low-alcohol wines offers significant growth opportunities, enabling winemakers to diversify their revenue streams and enhance profitability. Evolving regulations, especially in Europe, emphasize transparency in labeling and nutritional information, aligned with consumer preferences. Incorporating low-alcohol and nonalcoholic wines is a strategic move for winemakers, ensuring competitiveness and relevance in a changing market.

Accounting for circular economy principles in Life Cycle Assessments of extra-virgin olive oil supply chains
The paper by Grazia Cinardi et al. explores the application of circular economy (CE) principles within the extra-virgin olive oil (EVOO) sector using life cycle assessments (LCA). It aims to identify sustainable practices that reduce environmental impacts associated with olive oil production.

Wine waste valorisation: crushing the research domain
The paper, “Wine waste valorisation: crushing the research domain,” delves deeply into sustainability practices and the implementation of circular economy strategies in the wine industry. This highlights the urgent need for the wine industry to adopt sustainable and profitable methods for waste valorization, addressing both environmental and economic sustainability goals. This study conducted a systematic literature review of 67 scientific papers and additional grey literature to provide a comprehensive overview of current practices and gaps in the research.

The impact of the Mediterranean diet on immune function in older adults
Introduction For decades, epidemiologists have debated the limitations of traditional causal models of diseases that focus on the linear and sequential views of causality. The recent shift towards understanding the interplay between social, environmental, and biological factors in shaping health over a lifetime marks a significant evolution in public health approaches. Aging is not a…

Three decades of research on wine marketing
This comprehensive review examines the evolution and trends in wine marketing research over the past three decades, drawing on 1135 documents published between 1990 and 2022 from Web of Science and Scopus databases. This study identifies key themes and their development over time using bibliometric techniques, such as co-word analysis and bibliographic coupling. Early research focused on consumer behavior and pricing strategies, whereas recent years have seen an expansion in wine tourism, sustainability, and digital marketing. The findings highlight the growing importance of sustainability practices and the role of digital platforms in shaping consumers’ preferences. Key research themes include consumer behavior, wine quality, market segmentation, and sustainability, which reflect the industry’s response to evolving market dynamics and environmental challenges. This study underscores the multidisciplinary nature of wine marketing research, integrating insights from business, economics, food science, and environmental studies and provides a foundation for future research to develop effective marketing strategies in the global wine market.

A Narrative Review of Metabolomic Insights into Olive Oil’s Nutritional Value
This review explores the critical role of advanced metabolomic methodologies in interpreting the complex relationship between the bioactive compounds in olive oil and their health benefits. Olive oil, the cornerstone of the Mediterranean Diet, is renowned for its numerous health benefits including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and cardioprotective properties. This review begins with an overview of the importance of olive oil for nutrition and health, followed by a detailed discussion of the key metabolites that contribute to its therapeutic potential. It further explores the evolution of analytical techniques in metabolomics, from traditional methods to cutting-edge technologies, such as mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, which have enhanced our understanding of the complex composition of olive oil. This review highlights how these advanced analytical findings correlate with the known health properties of olive oil and presents case studies in which these methodologies have led to new insights. Finally, we address the challenges in standardizing these techniques and discuss future research directions, underscoring the significance of metabolomics in nutritional science and public health. This comprehensive analysis aims to provide a deeper understanding of the health benefits of olive oil, informed by the latest advancements in analytical methodologies

Viticulture and the European Union’s Common Agricultural Policy (CAP): Historical overview, current situation and future perspective
The paper emphasizes the importance of disseminating agroecological knowledge and implementing nature-based strategies to ensure the successful application of the CAP reforms. It calls for a collective awareness and effort from all societal sectors, including producers, consumers, and policymakers, to embrace environmental protection measures in agriculture. The paper also stresses the need to communicate effectively the benefits of biodiversity conservation and natural soil processes to accelerate the adaptation of agricultural systems to environmental challenges.

Enhancing employee wellbeing and happiness management in the wine industry
This research examines the connection between Green Human Resource Management (GHRM) and Sustainable Performance (SP) in Spanish wineries, emphasizing the mediating roles of Employee Wellbeing (EW) and Work Engagement (WE). This study is pertinent, given the growing focus on sustainability as a core business strategy. To refine the precision of the examined cause-effect relationships, variables such as the age and size of the winery and membership in a Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) are incorporated as controls. Utilizing a conceptual model informed by prior studies, this study employs structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) to analyze data from 196 wineries collected from September 2022 to January 2023. The findings highlight a positive and significant link between GHRM practices and the SP of these wineries, with EW and WE serving as partial mediators. The significance of this study lies in its contribution to the understanding of GHRM’s benefits in enhancing SP, particularly in the Spanish wine industry, a context not extensively explored in previous research. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to investigate the mediating effects of EW and WE on the GHRM-SP relationship in this sector, marking a notable advancement in this field.

