This post summarizes the results of a study aimed to investigate the effect of farming practices on the diversity of grape fungal community of Vitis vinifera L. cultivar Montepulciano and the microbial metabolic activity. The obtained results revealed that farming practices shape the fungal community influencing wine traits linking the wine with the viti-vinicultural area of origin.
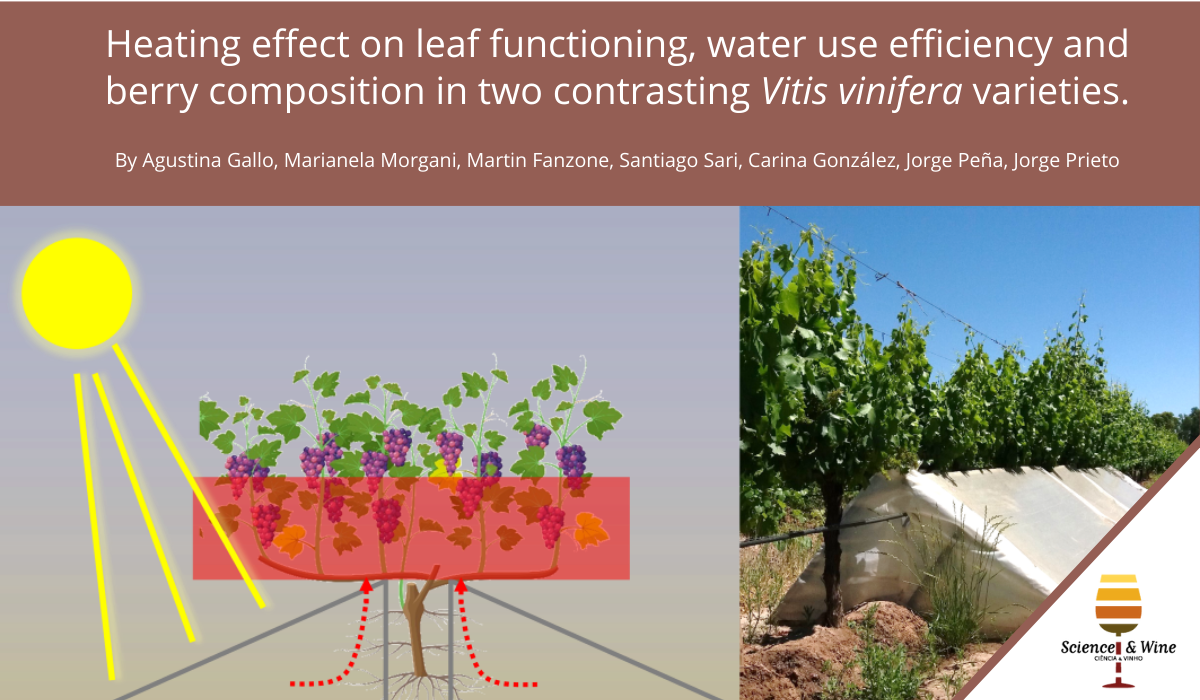
Heating effect on leaf functioning, water use efficiency and berry composition in two contrasting Vitis vinifera varieties.
Global warming will threaten vineyard sustainability in warm and arid regions. Therefore, increasing water use efficiency (WUE) is essential for long-term viticulture sustainability. Nevertheless, studies concerning the response of stomata and WUE to temperature are scarce. We evaluated the effect of sustained warming on WUE and its components in cultivars with contrasting stomatal behaviour.

5th Edition of the Wine Active Compounds (WAC) Congress, Dijon 2022
After two successive postponements, the fifth edition of Wine Active Compounds (WAC) 2021 happened in the Palace of the Dukes of Burgundy in Dijon, France, from Wednesday June 29 to Friday July 1, 2022, under the auspices of the UNESCO Chair “Culture & Traditions of Wines” and the Institut Jules Guyot at University of Burgund.

Increased temperatures due to climate change alter anthocyanin concentration and composition in berries of Malbec, Merlot, and Pinot Noir in a cultivar-dependent manner
Climate is determinant for grapevine geographical distribution, berry attributes, and wine quality. Due to climate change, a 2-4 °C increase in mean diurnal temperature is predicted by the end of the century for the most important Argentine viticulture region. The authors hypothesize that such temperature increase will affect color intensity and other quality attributes of red grapes and wines. The present study investigated the effect of high temperature (HT) on anthocyanin concentration and composition, pH, and resveratrol and solids content in berries of three major wine-producing varieties during fruit ripening in two seasons.

Explaining the influence of the ecosystem/viticulture in the Chilean Cabernet Sauvignon quality
Cabernet Sauvignon grapes in Chile, mainly grown between the 30° S and 36° S, account for more than 30% of Chilean wine production, and yield wines with different characteristics which influence their quality. The aim of this study was to apply a liquid chromatography—mass spectrometry (LC–MS)-based metabolomic protocol to investigate the quality differentiation in a sample set of monovarietal wines from eight valleys covering 679 km of the north-south extension. The results pointed out that N-containing metabolites (mainly small peptides) are promising biomarkers for quality differentiation. Moreover, the premium wines were characterized by higher amounts of anthocyanins and other glycosylated and acetylated flavonoids, as well as phenolic acids; standard quality wines, on the other hand, presented stilbenoids and sulfonated catabolites of tryptophan and flavanols.

Riesling or Spätburgunder wine – which one is more sustainable ?
The objective of the present study was to identify management strategies and carbon reduction potentials for a sustainable wine production based on the carbon footprint and the water footprint of locally grown grapes and wine locally produced and consumed.

HEKTOR – Heterogeneous autonomous robotic system in viticulture and mariculture
A heterogeneous robotic system that can perform various tasks in the steep vineyards of the Mediterranean region was developed and tested as part of the HEKTOR—Heterogeneous Autonomous Robotic System in Viticulture and Mariculture—project. This article describes the design of hardware and an easy-to-use method for evaluating the energy consumption of the system, as well as, indirectly, its deployment readiness level. The heterogeneous robotic system itself consisted of a flying robot—a light autonomous aerial robot (LAAR)—and a ground robot—an all-terrain mobile manipulator (ATMM), composed of an all-terrain mobile robot (ATMR) platform and a seven-degrees of-freedom (DoF) torque-controlled robotic arm. A formal approach is presented to describe the topology and parameters of selected vineyards It is shown how Google Earth data can be used to make an initial estimation of energy consumption for a selected vineyard. On this basis, estimates of energy consumption were made for the tasks of protective spraying and bud rubbing. The experiments were conducted in two different vineyards, one with a moderate slope and the other with a much steepest slope, to evaluate the proposed estimation method.

The relationship between grape ripening rate and wine quality
Grape ripening accelerates under warmer and drier conditions, resulting in the accumulation of sugars (‘technological’ maturity) being decoupled from phenolic and aromatic composition. This study investigated the effect of different rates of ripening on the composition of Cabernet Sauvignon and Riesling wines. By mapping grape and wine metabolites and exploring their relationship, the outcomes of this study demonstrate the importance of ripening rates in determining wine quality.
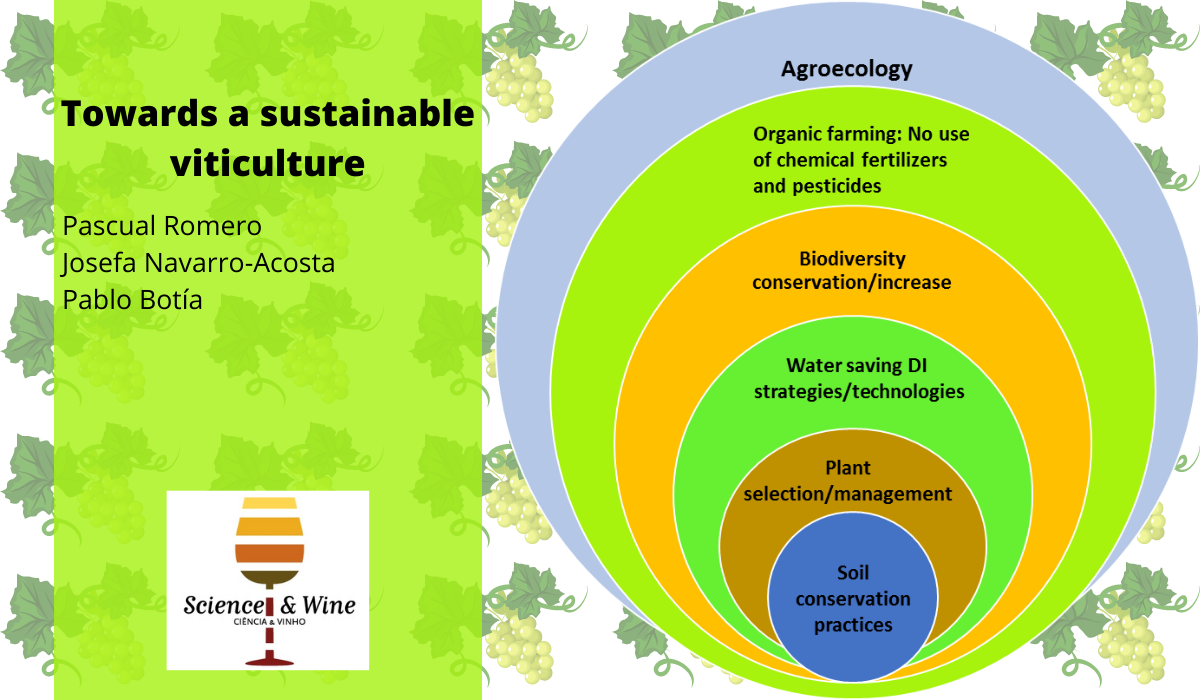
Towards a sustainable viticulture: The combination of deficit irrigation strategies and agroecological practices in Mediterranean vineyards. A review and update
This post summarizes a review of the state of the art of different physiologically-based water-saving irrigation strategies and methods used to improve productive water use efficiency and berry and wine quality in vineyards. Authors also show how these irrigation practices, combined with more sustainable soil management and other agroecological practices, can help to mitigate the negative effects of climate change on wine grapes cultivation and make irrigated Mediterranean vineyards more resilient and sustainable. The authors also review optimum vine water status ranges and the thresholds proposed for better deficit irrigation scheduling in vineyards. In addition. They consider sustainable soil management practices – such as cover crops, mulching, composting, reduced tillage, mutualistic plant-microorganisms interactions, and agroforestry . The idea is to design sustainable and climate-change-resilient agricultural systems (e.g. vineyards) in Mediterranean semi-arid areas.

Quality of Malvasia delle Lipari Sweet Wine influenced by bottle colour, light and storage temperature
The influence of light exposure, bottle color and storage temperature on the quality parameters of Malvasia delle Lipari (MdL) sweet wine were investigated. Wine samples bottled in clear-colored (colorless, green and amber) glass were stored under different artificial lighting conditions, in order to simulate the retail environment (one cool-white, fluorescent lamp) and to perform an accelerated test (four and six cool-white, fluorescent lamps). The storage temperature was kept constant (25 °C) for the first 90 days of the experiment and then samples were monitored for up to 180 days at higher temperatures (30, 35 and 40 °C). The principal enological parameters, total phenols, color, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) and 2-furaldehyde (2F) contents were studied. The shelf-life test pointed out minimum variations of the basic chemical parameters, while the quality attributes most affected by lighting were color, together with HMF and 2F levels which, hence, can be considered as indicators of the severity of storage conditions.

