Ever wondered about the utilisation of valuable remnants from the wine industry to revolutionise ceramics? A groundbreaking study published recently has opened the door to a new era in ceramic production, exploring the wine industry surplus in an unexpected and astonishing way! In this exciting study, researchers investigated the potential of incorporating grape skins into red ceramics to assess their impact on the physical and mechanical properties of the clayey body. Five different compositions were prepared, each with varying percentages of biomass incorporation:0, 2.5, 5, 7.5, and 10%. The specimens, crafted through vacuum extrusion in a laboratory extruder, were subjected to meticulous tests and analyses encompassing chemical, mineralogical, thermal, physical, morphological, and microscopic examinations of the clayey raw materials. This innovative approach not only contributes to sustainable practices by recycling wine industry by-products but also holds the promise of reshaping the future of ceramic production. By harnessing the potential of grape skins, we are not just creating ceramics; we are crafting greener, more sustainable tomorrow. Cheers to a future where the art of winemaking and ceramic craftsmanship intertwine, paving the way for a more eco-friendly and innovative world.

TANQUE: Transforming Agriculture for Nurturing Quality of Life and Understanding Ecology
We will continue to seek government support to sustain our organic agriculture practices and to restore the old hydraulic olive oil mill, which will serve as the focal point for all our educational, scientific, and cultural activities. How can you help? You can participate in the events organized by Science & Wine and purchase our products at: https://www.science-and-wine-conferences.com/. I would greatly appreciate any companies who are willing to lend their support to this project. Keep an eye out for news and updates. Thank you for your support!

Responsible Alcohol Consumption: A Call to Action
I decided to write this post after reading an article in the Portuguese newspaper, Expresso, which highlighted the negative health effects and cancer risks associated with the consumption of small amounts of alcohol. It is a personal reflection of a woman, mother, teacher, and scientist based on my perspective on the world and scientific evidence. Discussion about alcohol consumption? Yes, but for there to be results, common sense must prevail.

Alcohol Labelling: Promoting Consumer Health Awareness?
Ireland introduced legislation on May 22, 2023, requiring alcohol products to carry health warning labels. This aims to inform consumers about alcohol’s health risks. However, the effectiveness of such labels is debated, especially for wine due to its cultural significance, and according to scientific data beliefs in its health benefits may not be easily influenced by these warnings.

Revitalizing Local Communities through Project Capella
Discover how @Greengrape’s Projeto Capella is reshaping local development through sustainable initiatives. In this post we uncover the essence of Project Capella and its impact on local communities. Together, let’s embrace a journey towards sustainability, one step at a time.

The role of novel instruments of brand communication and brand image in building consumers’ brand preference and intention to visit wineries
A recent study suggests implications for theory and practice relative to brand management in terms of communication and image; and it proposes insights into novel communication tools and marketing activities for the winery tourism industry. Firms should employ a holistic evaluation of brand communication to involve the whole organization, which would enhance the strategic role that brand communication plays.

Food and Nutrition Literacy: Exploring the Divide Between Research and Practice
This study addresses the growing recognition of the importance of food and nutrition literacy, while highlighting the limited research in this field, particularly the gap between research and practice. Existing studies have primarily concentrated on defining and measuring food or nutrition literacy. Although interventions targeting food and nutritional literacy have shown promise in promoting healthy eating, further research is required to identify effective approaches in diverse populations and settings. This study emphasizes the need for additional research to measure intervention program efficacy to enhance the policies and practices in this critical area of public health. These findings underscore the importance of understanding food/nutrition literacy and developing effective interventions to promote healthy eating habits. By bridging the research–practice divide, this study provides valuable insights for policymakers, practitioners, and researchers to address the gaps and improve food/nutrition literacy in various contexts.
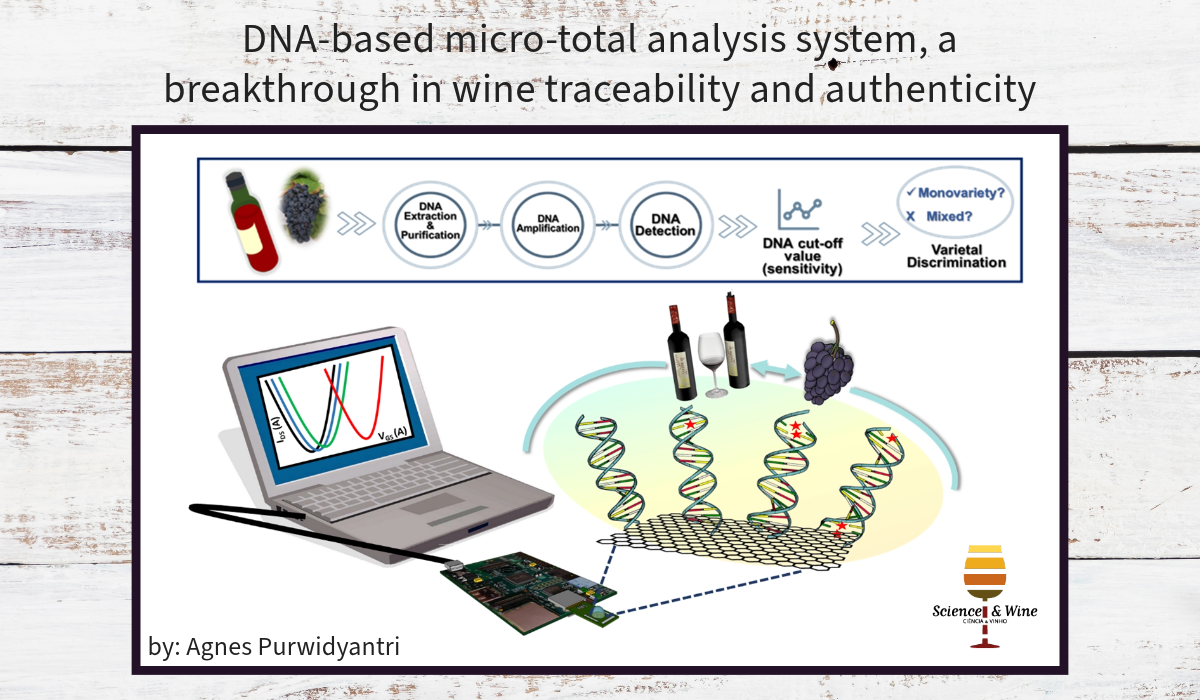
DNA-based micro-total analysis system, a breakthrough in wine traceability and authenticity
For the first time, it was presented a DNA-based analytic tool for grapevine varietal discrimination using an integrated portable biosensor based on a monolayer graphene field-effect transistor array. The system comprises a wafer-scale fabricated graphene chip operated under liquid gating and connected to a miniaturized electronic readout. The platform can distinguish closely related grapevine varieties, thanks to specific DNA probes immobilized on the sensor, demonstrating high specificity even for discriminating single-nucleotide polymorphisms, which is hard to achieve with a classical end-point polymerase chain reaction or quantitative polymerase chain reaction. The reported biosensor provides a promising way toward developing decentralized analytical tools for tracking wine authenticity at different points of the food value chain, enabling data transmission and contributing to the digitalization of the agro–food industry.

Ancient DNA analysis of winegrape seeds reveals genetic link between two modern varieties of red and white grapes and grape varieties cultivated some 1,100 years ago
One ancient seed was found to belong to the Syriki variety, still used to make red wine in Greece and Lebanon. Since winegrapes are usually named after their place of origin, it is quite possible that the name Syriki is derived from Nahal Sorek, an important riverbed in the Judean Hills. A second seed was identified as related to the Be’er variety of white winegrapes still growing in the sands of Palmachim on Israel’s southwestern Mediterranean seashore.

The vineyard yeast populations are influenced by… forests and wasps. [Forests influence yeast populations vectored by insects into vineyards]
In the vineyard, yeast communities impact the ripening and fermentation of grapes and are influenced by geographical location, climate, and soil characteristics. Despite the great advancement in our knowledge of the vineyard mycobiota, a key step of the process leading to the definition of the vineyard yeast community is still poorly understood: if geography, climate, and soil influence the mycobiota, potentially through selection, where do the yeast originate from, and how can they reach the vineyard? In this perspective, it is currently acknowledged that forests host several yeast species and that insects, particularly social wasps, can vector and maintain the yeasts known to populate the vineyard. Alas, the conveyance, fostered by insects, of yeasts from the forest to the vineyard has not been proven yet. In this study, we aimed to assess the existence of links between a potential natural source of yeasts (woods), the vectors (social wasps), and the composition of the vineyard mycobiota.

