Exploring the magic of the Mediterranean Diet during Christmas! 🎄 Dive into the rich traditions and conviviality captured by Elisabetta Moro and Rossella Galletti in their captivating chapter “Sharing Food and Conviviality in the Mediterranean Diet.” 📖✨ Discover how festive feasts create bonds, not just through food but also through shared moments. Experience the enchantment of the Neapolitan Christmas banquet and learn how it weaves a tale of community, love, and timeless traditions

High Extra Virgin Olive Oil Consumption Is Linked to a Lower Prevalence of NAFLD with a Prominent Effect in Obese Subjects
Unlock the secret to a healthier life with Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO)! 🌿 Recent research reveals its powerful impact on liver health, specifically in combating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). 🫒 Dive into the study findings: High EVOO consumption is linked to a remarkable 26% reduction in NAFLD risk for our friends dealing with obesity! 💪✨ Whether you’re aiming for wellness or battling the bulge, let EVOO be your ally. 🍽️ Embrace the goodness and savor the journey to a healthier you!

Nutrition and Food Literacy: Framing the Challenges to Health Communication
In a world beset by misinformation regarding nutrition, it is imperative to embark on a quest for #FoodLiteracy. A thorough understanding of the impact of dietary choices is paramount for leading a healthy life. The proliferation of false information on social media is a significant impediment to making informed decisions about food. To counteract this, it is crucial to exercise caution, seek credible sources, and base our choices on sound knowledge. Effective communication is fundamental to promoting good health. By striving to improve #HealthLiteracy, we can decipher nutritional facts and empower ourselves to make informed decisions about food. This is not just individual responsibility; it is a collective effort. Sharing this post can help raise awareness and build a community committed to better health through informed food choices.

Enhance Wine Production Potential by Using Fresh and Dried Red Grape and Blueberry Mixtures with Different Yeast Strains for Fermentation
Our colleague Juan Martín-Gómez from Universidad de Córdoba, Spain presented a fascinating research study on the ‘Sustainability of wine production and food systems in the Mediterranean region’ at the 3rd World Science & Wine Congress. This study focused on replacing traditional sun-drying methods in Mediterranean winemaking with controlled-airflow chamber-drying. This alternative technique improves the quality, phenolic content, and antioxidant properties of red grapes and blueberries. Furthermore, the post encourages researchers to consider submitting their work to a special joint issue. Because these issues are interdisciplinary, authors are given the flexibility to choose from several participating journals based on their research scope. The options include Foods; Sustainability; IJERPH; Agriculture.

Insights from the INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC CONGRESS: LIFESTYLE, DIET, WINE & HEALTH II
Thrilled to announce the launch of our latest article summarizing insights from the prestigious INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC CONGRESS: LIFESTYLE, DIET, WINE & HEALTH, held in Toledo, Spain!
Dive deep into the world of nutrition, exercise physiology, and culinary arts as leading experts share groundbreaking findings on how lifestyle choices shape our health. Discover the secrets behind the Mediterranean Diet, the impact of physical activity on gene expression, and the fascinating link between movement behaviors and appetite control.

Insights from the INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC CONGRESS: LIFESTYLE, DIET, WINE & HEALTH I
From Toledo, Spain: Insights on alcohol, health, and wine’s wonders! Experts discussed alcohol’s nuances, revealing its role in heart health. Studies show moderation is key. Stay tuned for more groundbreaking findings in Science & Wine!
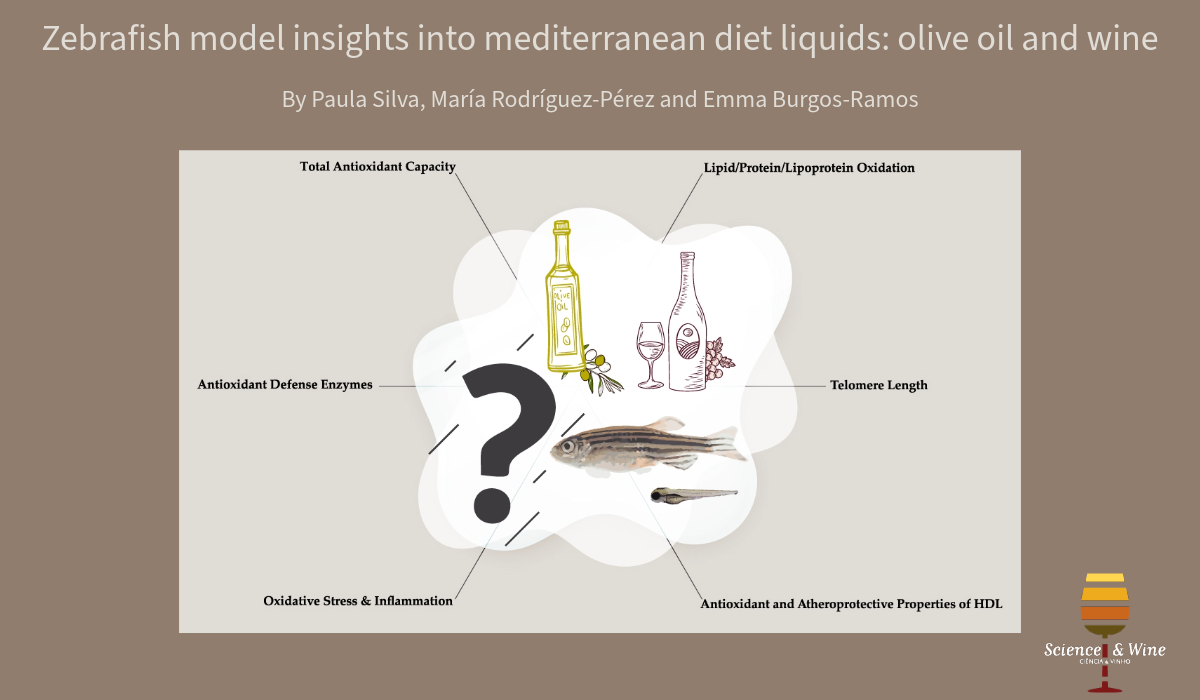
Zebrafish Model Insights into Mediterranean Diet Liquids: Olive Oil and Wine
We are thrilled to announce this week’s blog post on Science & Wine, dive into the fascinating world of antioxidants and the Mediterranean diet, as we proudly present our latest review published in the renowned MDPI Antioxidants Journal. In this groundbreaking review, we embarked on a journey through the intricate universe of age-related diseases, particularly cardiovascular conditions. We delved deeply into the powerful effects of two Mediterranean diet superheroes: Olive Oil and Wine! Our exploration ranged from intriguing observational studies to cutting-edge preclinical experiments, paving the way for potential translational breakthroughs in zebrafish experimentation. Why Zebrafish? Ever wondered how tiny fish could hold the key to understanding the health issues of olive oil and wine. The astonishing genetic proximity of zebrafish to humans offers a unique gateway to unravel the mysteries of these Mediterranean marvels. This review sheds light on the immense potential of zebrafish as an experimental model, urging scientists worldwide to fully harness its power. Let us explore the uncharted territories together, pushing the boundaries of knowledge and advancing our understanding of age-related disease prevention within the Mediterranean dietary framework.

Nutrition literacy status and its association with adherence to the Mediterranean diet, anthropometric parameters and lifestyle behaviours among early adolescents
As the new school year begins, families are faced with the usual daily preparations. Questions arise about what lunch choices kids will make and what snacks they’ll consume. Parents of teenagers often assume their children can handle these decisions independently. But are they truly capable? What is the level of food literacy among our youth, and have we adequately prepared them for independence and autonomy? In this context, I came across an article published in August titled “Nutrition literacy status and its association with adherence to the Mediterranean diet, anthropometric parameters, and lifestyle behaviors among early adolescents.”

TANQUE: Transforming Agriculture for Nurturing Quality of Life and Understanding Ecology
We will continue to seek government support to sustain our organic agriculture practices and to restore the old hydraulic olive oil mill, which will serve as the focal point for all our educational, scientific, and cultural activities. How can you help? You can participate in the events organized by Science & Wine and purchase our products at: https://www.science-and-wine-conferences.com/. I would greatly appreciate any companies who are willing to lend their support to this project. Keep an eye out for news and updates. Thank you for your support!

Responsible Alcohol Consumption: A Call to Action
I decided to write this post after reading an article in the Portuguese newspaper, Expresso, which highlighted the negative health effects and cancer risks associated with the consumption of small amounts of alcohol. It is a personal reflection of a woman, mother, teacher, and scientist based on my perspective on the world and scientific evidence. Discussion about alcohol consumption? Yes, but for there to be results, common sense must prevail.

