Virgin olive oil (VOO) is the main fat consumed by populations in the Mediterranean basin, and phenolic compounds, minor components of this fat, are known to be responsible for diverse health benefits when consumed in a regular diet. According to numerous investigations, these benefits are mostly related to phenols such as tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol and secoiridoid derivatives such as ligstroside, oleuropein, oleocanthal and oleacein. These compounds are present in low concentrations, and for some of them, standards are not commercially available, hampering studies on the mechanisms underlying their biological activity. In order to contribute to a better knowledge of the bioactivity of these compounds and their metabolites, they must be available with high purity and in sufficient amounts for the assays. Chemical synthesis has been considered a convenient way to obtain these compounds. This Review will focus on the synthesis of representative VOO compounds, namely, ligstroside, oleuropein, oleocanthal, oleacein and analogues.

Extra Virgin Olive Oil: Thermal Effects vs Region of Cultivation
Extra virgin olive oil is one of the superlative due to its health benefits. In this work, the Fluorescence spectra of extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) from different olive growing regions of Pakistan and Al-Jouf region from the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) were obtained. The results demonstrated fluorescence spectroscopy as a quick, cost-effective and reliable approach to assess the quality and thermal stability of EVOO. These characteristics of fluorescence spectroscopy may lead to the development of portable device for the onsite monitoring of EVOO.

Beneficial effects of extra virgin olive oil on skin wound healing
Hydroxytyrosol and oleic acid-induced reactive nitrogen species promotes the activation of the Nrf2 pathway leading to a promotion of fibroblast survival and migration that are essential for the resolution of wound healing.

The Mediterranean Diet: An Update of the Clinical Trials
The Mediterranean Diet (MedDiet) is a term used to identify a dietary pattern originating
from the unique multi-millennial interplay between natural food resources and the eating practices
of people living in the Mediterranean basin. The majority of MedDiet’s beneficial effects could be primarily related to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties as well as the effectiveness of this dietary pattern in controlling waist circumference and obesity. Moreover, strict, and long-lasting adherence to the MedDiet as well as the beneficial effects of specific components (e.g., olive oil or its polyphenols) seem to emerge as useful insights for interventional improvements. These findings present further insights into the MedDiet’s resources and how it could strengthen overall public health.

3rd World Science & Wine: Sustainability of wine production and food systems in the Mediterranean region
As promised, we will maintain the organization of the World Congress every two years. The 3rd World Science & Wine Congress will be from 14 to 16 June 2023 in Vila Nova De Gaia and the Douro region. The topic for this scientific meeting here will be “Sustainability of wine production and food systems in the Mediterranean region”.

Interest of polyphenols in the prevention of age-related diseases and in regenerative medicine
7-ketocholesterol and 7β-hydroxycholesterol are two oxysterols mainly formed by the autoxidation of cholesterol. These two molecules are interconvertible via specific enzymes. These two oxysterols are often observed at increased amounts in biological fluids as well as tissues and organs affected during age-related diseases and in diseases of civilization such as cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and ocular diseases as well as type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Many nutrients present in significant amounts in the Mediterranean diet, especially tocopherols, fatty acids, and polyphenols, have shown cytoprotective activities as well as several Mediterranean oils (argan and olive oils, milk thistle seed oil, and pistacia lentiscus seed oil). Consequently, a nutraceutical approach, rich in nutrients present in the Mediterranean diet, could thus make it possible to counteract certain age-related and civilization diseases associated with increased levels of 7-ketocholesterol and 7β-hydroxycholesterol.
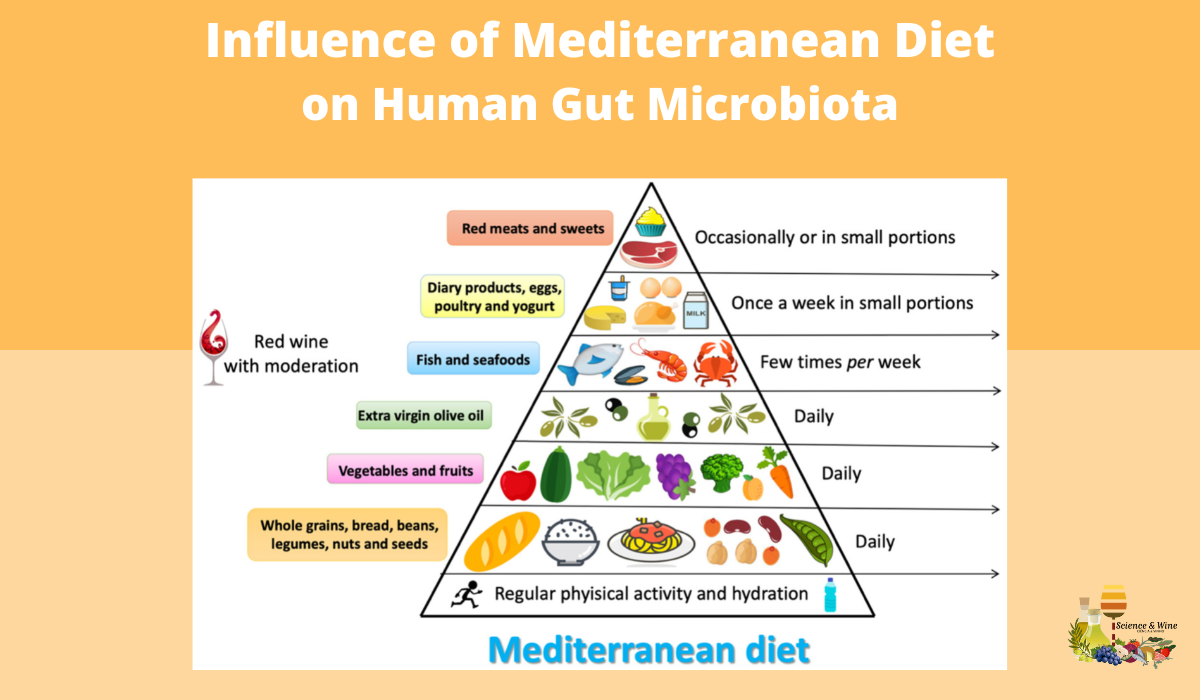
Influence of Mediterranean Diet on Human Gut Microbiota
Gut microbiota changes correlate with health status. Literature data on gut microbiota show that all dietary changes can induce the alteration of gut microbiota composition. Mediterranean diet (MD) is associated with a reduction of all-cause mortality and in this review, Giuseppe Merra and collaborators analyzed its interactions with human microbiota. In particular, they explored the modulation of the human microbiota, in response to MD adherence, focusing the attention on polyphenols, polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA)ω-3 and fiber. Evidences suggest that MD is able to modulate the gut microbiota, increasing its diversity. In fact, a Mediterranean-type dietary pattern is associated with specific gut microbiota characteristics. The available evidence, suggests that gut microbiota of subjects that follow a MD is significantly different from subjects that follow a Western diet model.

Olive oil and exercise: sharing the same path to better health?
An olive oil (OO) rich diet or high-intensity interval training (HIIT) independently improve markers of health and energy metabolism, but it is unknown if combining OO and HIIT synergize to improve these markers. This study characterized the isolated and combined impact of OO and HIIT on markers of health and energy metabolism in various tissues in C57BL/6J female mice. The results highlight the pleiotropic effects of OO and HIIT, although their combination does not synergize to further improve most markers of health and energy metabolism.

Separation and Determination of Biophenols in Olive Oil Samples Based on the Official Method of the International Olive Council and Commission Regulation (EU) No. 432/2012
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the key quality characteristics of olive oil with a main focus on the biophenolic content, its beneficial effects on health and the contribution of various quality characteristics to its health claims, as well as its influence from various parameters.

Food Habits of the Mediterranean Diet are Associated with Better Metabolic Features in Youths with Type 1 Diabetes
The aim of this study was to evaluate adherence to the Mediterranean diet (MedDiet) among children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes (T1D) in relation to metabolic control. Adherence to the MedDiet was assessed with the Mediterranean Diet Quality Index (KIDMED) questionnaire and physical activity by the International Physical Activity Questionnaire for Adolescent (IPAQ-A) on 65 subjects (32 males, 9–18 years) with T1D. The promotion of the MedDiet, mainly having a healthy breakfast, is a good strategy to include in the management of T1D to improve glucose and metabolic control. This research is valuable for parents to obtain the best results for their children with T1D.

